MPC Maintains Repo Rate
On 1st October, 2025, the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), has announced its Monetary Policy Statement. MPC has opted to maintain the key interest rate, i.e., Repo Rate . Let us see the MPC statement in detail now.
MPC Maintains Repo Rate – Monetary Policy Statement, October 2025
The key policy rate, also known as the repo rate, was unanimously maintained by the MPC at 5.50%.
Consequently, the Bank Rate and Marginal Standing Facility will stay at 5.75% percent, while the Standing Deposit Facility (SDF) rate will be modified to 5.25%.
The decision supports growth while also achieving a medium-term CPI inflation objective of 4% with a +/- 2 percent band. .
The MPC continues to adopt a neutral policy position. .
MPC on Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Estimates
The global economy in 2025 has shown resilience with strong growth in the US and China, but uncertainty remains due to policy changes. Inflation is above target in some advanced economies, creating challenges for central banks. Financial markets are volatile, with the US dollar strengthening and treasury yields rising. Equities have remained strong in both advanced and emerging markets.
The strong economic performance in the first quarter of 2025-26, with real GDP growing at 7.8% driven by private consumption and fixed investment. Gross value added (GVA) also grew at 7.6%, led by manufacturing and services.
High frequency indicators show resilience in economic activity, with strong rural demand due to a good monsoon and robust agriculture activity.
Urban demand is gradually recovering. Government revenue expenditure has seen robust growth, and investment activity remains healthy despite some moderation in capital goods production and imports. Manufacturing sector is recovering, and services activity is maintaining momentum.
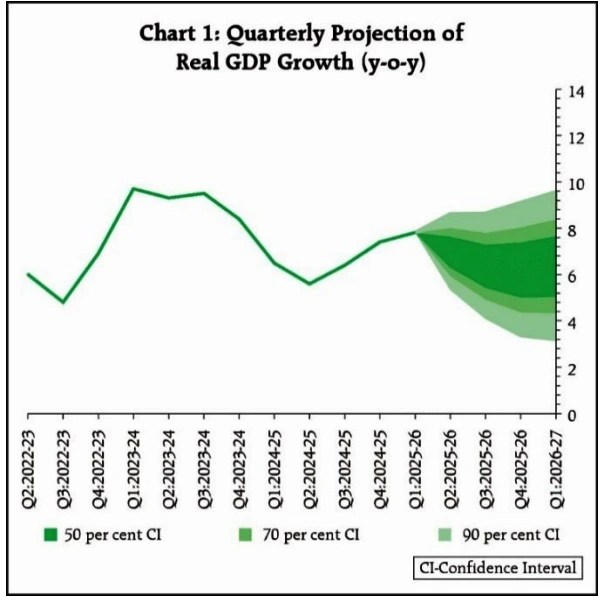
Source: MPC Statement, RBI
The current positive outlook for agriculture and rural demand due to an above-normal monsoon and good progress of kharif sowing. It also mentions supportive factors for demand such as buoyancy in the services sector and steady employment conditions.
However, uncertainties in tariff and trade policies, geopolitical tensions, and volatility in international financial markets pose downside risks to growth.
Despite these challenges, the implementation of growth-inducing structural reforms is expected to offset some of the adverse effects. Real GDP growth for 2025-26 is projected at 6.8%, with risks evenly balanced.
MPC on Inflation
The headline CPI inflation decreased to 1.6% in July 2025 before rising to 2.1% in August, driven by a decline in food inflation. Fuel group inflation remained stable, while core inflation was contained at 4.2% in August.
The inflation outlook for the second half of 2025-26 is expected to be softer than projected due to factors such as the south-west monsoon, higher kharif sowing, and GST rate cuts.

Source: MPC Statement, RBI
However, large base effects may lead to upward pressure on inflation in Q4. Overall, CPI inflation for 2025-26 is now projected at 2.6%.
MPC Stance
The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) has observed that inflation outlook has improved, with headline inflation revised lower for 2025-26. Despite weak external demand, growth outlook remains resilient due to domestic drivers and other factors.
However, growth projections for Q3 and beyond may be slightly lower due to tariff-related developments. Global uncertainties and tariff issues may also impact growth in the future.
The MPC has noted that policy space exists to support growth further, but will wait for the impact of current policy actions to unfold before making any further decisions.
The MPC therefore decided unanimously to maintain the policy repo rate at 5.5%.
The MPC also made the decision to maintain its impartial position. Nonetheless, two members, Prof. Ram Singh and Dr. Nagesh Kumar, believed that the neutral position should be modified to one that is more accommodating.
Additional Measures
- Strengthening the resilience and competitiveness of the banking sector
The Expected Credit Loss (ECL) framework of provisioning with prudential floors will be applicable to all Scheduled Commercial Banks and All India Financial Institutions from 1st April 2027.
They will have a glide path until March 31, 2031 to adjust to higher provisioning. Revised Basel III capital adequacy norms will also be effective for commercial banks from the same date.
A draft of the Standardised Approach for Credit Risk will be issued soon, with lower risk weights expected to reduce capital requirements for certain segments. Measures are being taken to align guidelines with international standards and strengthen the capital adequacy framework.
A draft circular on Forms of Business and Prudential Regulation for Investments has been finalized, with regulatory restrictions on business overlap being removed.
Risk-based deposit insurance premiums are proposed to incentivize sound risk management by banks and reduce premiums for better-rated banks.
- Promoting Ease of Doing Business
There are two key proposals: consolidation of circulars and directions for regulated entities; and providing greater flexibility to banks for opening and maintaining transaction accounts of borrowers.
Additionally, measures are proposed to strengthen the export sector, including extending the time period for repatriation from foreign currency accounts, increasing the period for forex outlay for Merchanting Trade transactions, and simplifying the process of reconciliation of outstanding entries related to exports and imports.
- Internationalising Indian Rupee
The progress made in using the Indian Rupee for international trade and proposes three measures to further promote its use. These measures include allowing banks to lend in Indian Rupees to non-residents from Bhutan, Nepal, and Sri Lanka, establishing transparent reference rates for major trading partner currencies, and expanding the use of SRVA balances for investment in corporate bonds and commercial papers.
My Perspective and Takeaways
Despite a challenging external environment, the Indian economy is still expected to achieve high growth. Inflation has decreased, allowing for monetary policy to support growth without compromising on price stability.
The MPC will assess the impact of recent policy changes before making a decision. India aims to achieve Viksit Bharat by its 100th year of independence through collaborative fiscal, monetary, regulatory, and public policies.
The recent simplification of the GST rate structure is a welcome change. Monetary policy will remain cautious, prioritizing price stability and supporting growth through clear communication and credible actions.
The MPC Statements clearly show that the RBI continues to prioritize managing inflation. Since the RBI has undertaken frontloading policies on the rate cut this year, the current policy stance and maintaining the repo rate at its current level are expected.
